Serological Pipets: Introduction, Design, and Diverse Applications in Laboratory Science
Abstract: Serological pipets are indispensable tools in laboratory science, designed for precise and controlled liquid transfer. This article provides an in-depth introduction to serological pipets, discussing their construction, calibration, and detailing the breadth of applications they serve across various scientific disciplines.
1. Introduction: Serological pipets are fundamental instruments in analytical laboratories, facilitating accurate and efficient liquid handling. Their ability to precisely measure and transfer liquids makes them essential for applications ranging from clinical diagnostics to research experiments. This article presents a comprehensive overview of serological pipets, exploring their design, calibration, and the wide spectrum of applications they support.
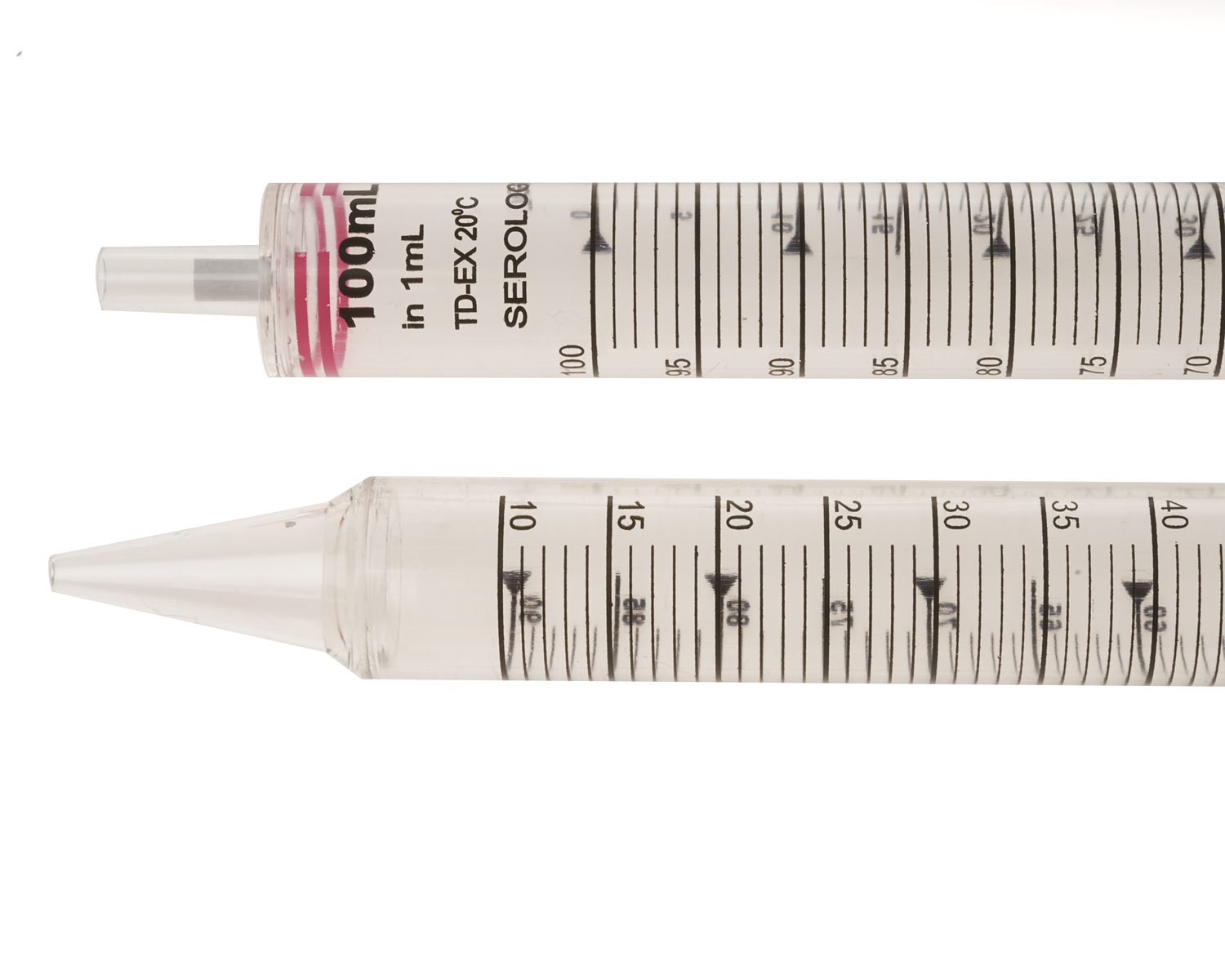
2. Design and Structure: Serological pipets typically consist of a transparent, elongated tube with calibrated volume markings along its length. The pipet’s lower end tapers to a fine tip, allowing for controlled liquid dispensing. Some models include a cotton or foam plug to prevent contamination and ensure consistent aspiration.
3. Calibration and Graduations: Accurate liquid transfer relies on precise calibration. Serological pipets are calibrated according to international standards, ensuring accuracy in volume measurements. Graduations on the pipet indicate incremental volume levels, often in microliters (μL) or milliliters (mL), allowing users to select desired volumes based on their experimental requirements.
4. Types of Serological Pipets: Serological_pipets come in various volumes, catering to different liquid transfer needs. Common sizes range from 1 mL to 50 mL, accommodating a broad spectrum of sample volumes. Disposable, sterile, and reusable options are available, each tailored to specific applications.
5. Applications of Serological Pipets:
5.1. Cell Culture and Microbiology: Serological_pipets are instrumental in cell culture workflows, enabling accurate media and reagent dispensing. They also play a vital role in microbial research, aiding in the precise transfer of bacterial or viral suspensions.
5.2. Clinical Diagnostics: In clinical laboratories, serological_pipets are used for sample aliquoting and reagent dispensing during diagnostic procedures. Their accuracy and reproducibility are crucial for reliable test results.
5.3. Molecular Biology and Genetics: Serological_pipets facilitate DNA and RNA extraction, PCR setup, and gel loading. Their ability to transfer small volumes of nucleic acids is essential for molecular biology experiments.
5.4. Biochemical Assays: Enzyme assays, immunoassays, and protein quantification techniques rely on precise liquid handling. Serological_pipets ensure accurate reagent addition and sample transfer.
5.5. Drug Discovery and High-Throughput Screening: In pharmaceutical research, serological_pipets aid in compound dispensing, enabling high-throughput screening of potential drug candidates.
5.6. Chemical Analysis: Serological_pipets find application in analytical chemistry for accurate preparation of standards, titrations, and sample dilutions.
6. Good Pipetting Practices: Achieving accurate results requires adherence to good pipetting practices. This includes proper pipet handling, maintaining vertical orientation, and using appropriate techniques to minimize liquid retention and contamination.
7. Conclusion: Serological pipets are essential tools that underpin numerous scientific endeavors. Their precision, versatility, and ease of use make them integral to laboratory workflows across a multitude of disciplines. As research continues to advance, serological_pipets will remain indispensable for ensuring reliable and reproducible liquid handling in diverse scientific applications.
 Buy now $165.96
Buy now $165.96 Buy now $169.49
Buy now $169.49 Buy now $79.46
Buy now $79.46 Buy now $88.40
Buy now $88.40 Buy now $165.38
Buy now $165.38 Buy now $234.22
Buy now $234.22







