TLC Selection Guide
| Sorbtech Normal Phase TLC Plate Selection Guide | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| TLC Plate Type | Description | Features | Types Available |
| Features an organic binder system resulting in a standard hardness of the silica layer. | Outstanding abrasion resistance can mark a plate with a lead pencil. Prevents damage when handling or transporting plates. Has a bright UV indicator. | ✓ Glass – Plastic – Aluminum ✓ Indicator ✓ w/o Indicator |
|
| Features a newly developed binder system, resulting in an outstanding hardness of the silica layer. | Outstanding abrasion resistance can mark a plate with a lead pencil. Prevents damage when handling or transporting plates. UV indicator utilized permits increased sensitivity for trace analysis. | ✓ Glass – Plastic – Aluminum ✓ Indicator ✓ w/o Indicator |
|
| Features an abrasion-resistant surface with outstanding dyeability. | Excellent separation efficiency due to optimized particle size distribution. Outstanding dyeability and abrasion resistance. | ✓ Glass – Plastic – Aluminum ✓ Indicator ✓ w/o Indicator |
|
| This is a soft layer plate that uses Gypsum as its binding agent. | For use in QC labs to adhere to European Pharmacopeia recommendations and as an alternative to organic binders used in traditional TLC plates. This softer binder permits easier scraping of the plate to isolate compounds. | ✓ Glass ✓ Plastic – Aluminum ✓ Indicator ✓ w/o Indicator |
|
| This is a soft layer plate that uses gypsum as its binding agent. Enhanced to bind specifically to the aluminum backing | Aluminum backed plates with minimized flaking of the coating permits easy cutting without damage to the plate. Outstanding wettability for precise colorization results, even with 100% aqueous detection reagents. | – Glass – Plastic ✓ Aluminum ✓ Indicator ✓ w/o Indicator |
|
| These plates contain a concentration zone serving as a “quick application zone”, which allows a quantitative evaluation of chromatograms. | Permits large volumes of dilute solutions to be applied. Reduces sample application error and evaporation time of sample when compared to traditional TLC plates, sharp bands produced. | ✓ Glass – Plastic ✓ Aluminum ✓ Indicator ✓ w/o Indicator |
|
HPTLC |
Contains a specific pore volume of 0.75 ml/g and particle size of 2-10 µm. | Narrow fractionation of silica particles allows sharper separations, shorter developing times, shorter migration distances, and increased detection sensitivity. | ✓ Glass – Plastic ✓ Aluminum ✓ Indicator ✓ w/o Indicator |
| Aluminum Oxide layer with a pH of about 6-8. Recommended when separation involves relatively nonpolar analytes. | Use for absorption chromatography for terpenes, alkaloids, steroids, and aromatic compounds. Excellent separation of basic and neutral compounds. | ✓ Glass ✓ Plastic ✓ Aluminum ✓ Indicator ✓ w/o Indicator |
|
Evaluation of a TLC chromatogram
The evaluation depends on the purpose of the chromatographic analysis. For qualitative determinations often localization of substances is sufficient. This can be easily achieved by parallel runs with reference standards. A parameter often used for qualitative evaluation is the Rf value (retention factor) or the 100-fold value hRf
The Rf value is defined as follows:
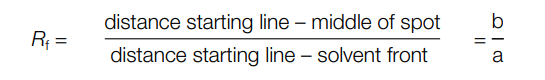

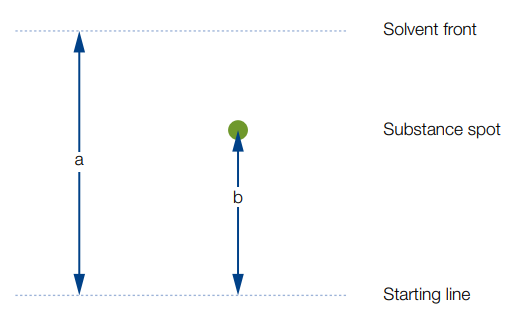
For example, your Rf values are between 0 and 1 but are best between 0.1 and 0.8 (i.e. 10–80 for hRf). If reproducible Rf values are to be obtained, several parameters such as chamber saturation, the composition of solvent mixtures, temperature, etc. must be strictly controlled.





