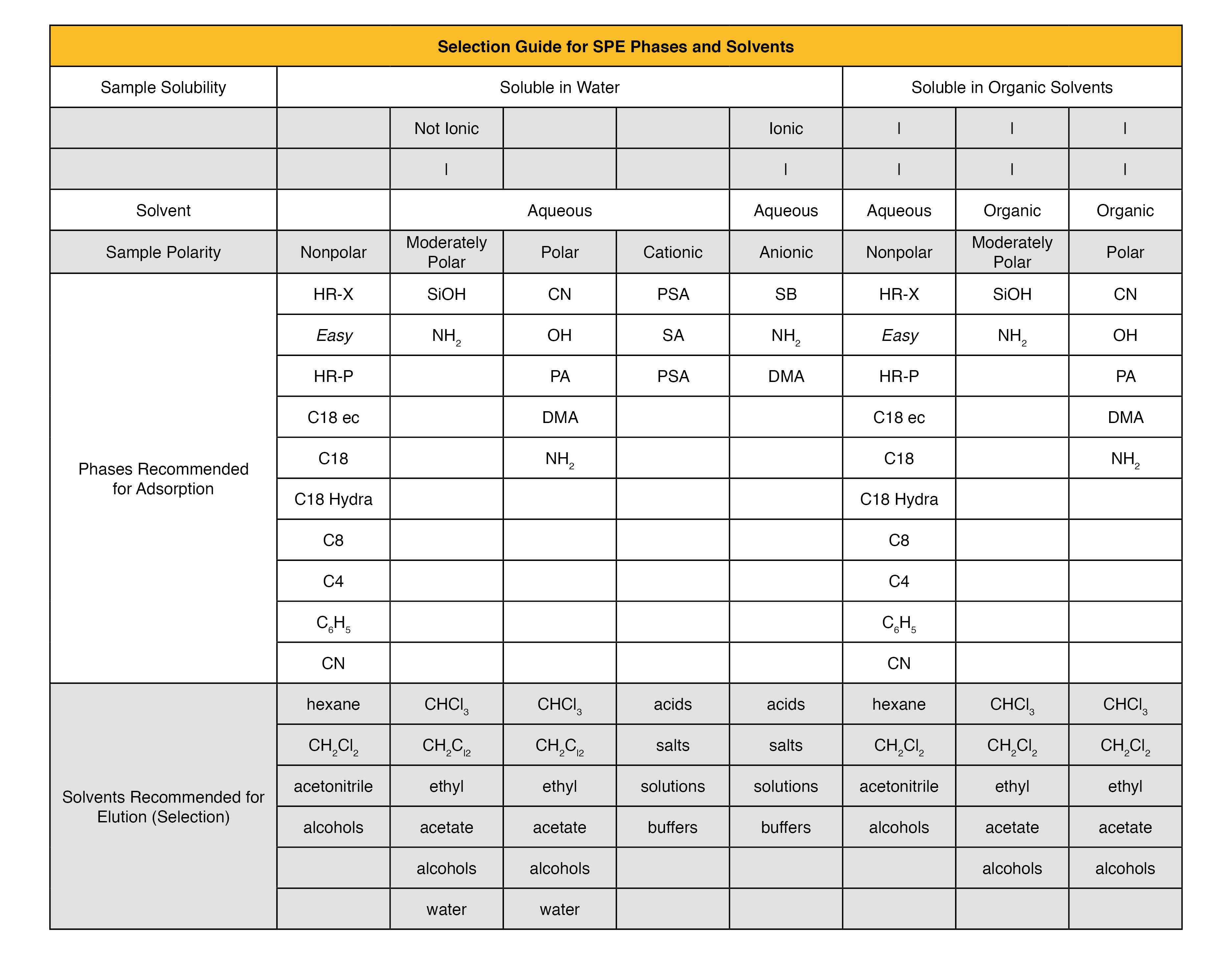
Chromabond® and Chromafix®
SPE – Solid Phase Extraction Cartridges
Proven performance in SPE since 1987
Macherey-Nagel SPE products high purity SPE cartridges for sample preparation provide an economical and effective solution for isolation and purification of your sample before downstream analytical instrument methods.
Our SPE cartridges are available as adsorbents based on polymer resins, surface-modified silica materials as well as Florisil®, polyamide, and aluminum oxide.

Choose the best phase for applications in pharmaceutics, environmental analysis, and ion chromatography.
CHROMABOND® SPE is offered in an extraction column format (polypropylene or glass) as CHROMAFIX® cartridges with Luer fittings (sizes S, M, L (0.4 – 1.8ml)) or as 96 well-filtration plates.
Features of Chromabond® and Chromafix® SPE Portfolio
- Wide range of over 25 adsorbents to meet any application need
- Column, well plate, and cartridge formats
- Highly reproducible recovery rates; cartridge to cartridge, lot to lot
- Available in silica and polymer-based phases for reverse phase, ion exchange, and specific-application needs
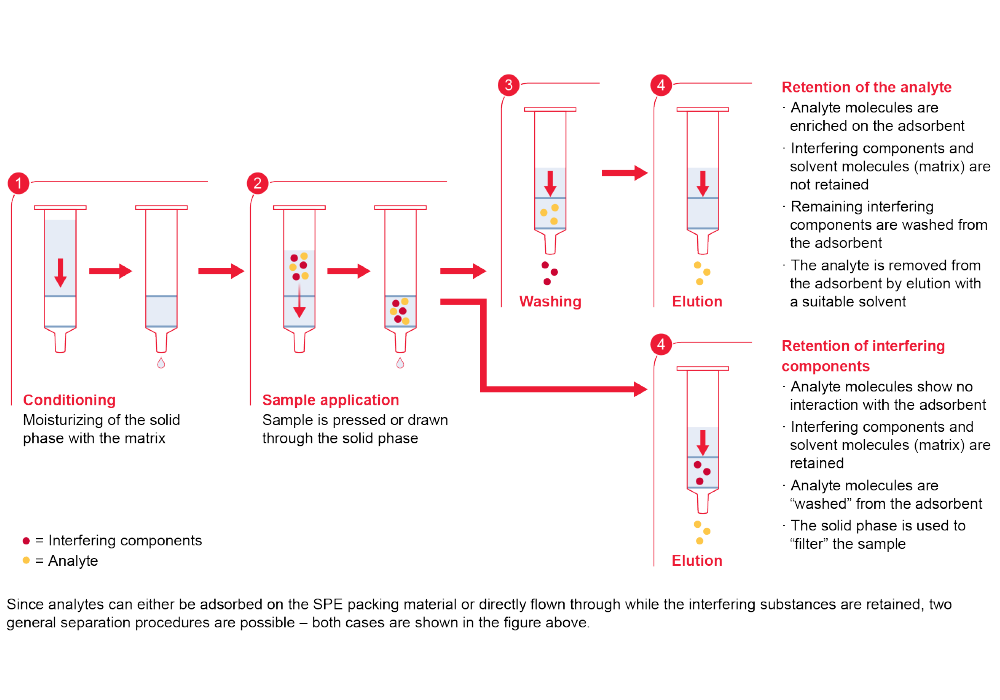
Molecular interactions in SPE
SPE adsorbents are most commonly categorized by the nature of their primary interaction mechanism with the analyte of interest. The three most common extraction mechanisms used in SPE are reversed-phase (RP), normal phase (NP) and ion exchanger.
Typical Extraction Mechanisms:
- Reversed-Phase Extraction of hydrophobic or polar organic analytes from an aqueous matrix
- Normal Phase Extraction of polar analytes from nonpolar organic solvents
- Ion Exchanger Extraction of charged analytes from aqueous or non-polar organic samples
Types of Retention Mechanisms
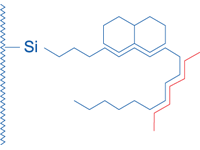 |
Nonpolar interactions
|
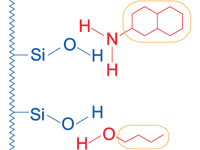 |
Polar interactions
|
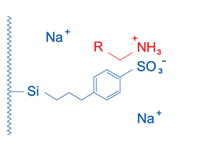 |
Cation Exchangers
|
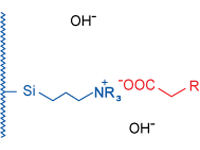 |
Anion Exchangers
|
It should be noted, that in SPE the interactions described above are not found in pure form, but in combination. For example, modified silicas, unless they have been subjected to endcapping (silanization of residual silanol groups with short-chain silanes), still possess free silanol groups, which can enter into secondary interactions.
Sample Pretreatment
For direct extraction with adsorbents the sample matrix (sample environment) has to fulfill three conditions:
- The matrix has to be liquid, if possible with low viscosity
- Solids should be removed from the liquid matrix
- The matrix (sample environment) should be suitable for retention of the analyte
For solid samples there are different methods to convert the sample into a suitable matrix:
- Dissolution of the solid sample in a suitable solvent
- Lyophilisation of the sample and dissolution in a suitable solvent
- Extraction of the solid sample with a suitable solvent
- Homogenization of the sample in a suitable solvent
In order to find the suitable solvent, one has to consider all desired sample components. Also, a suitable solvent should enhance the retention of the analyte. For example, samples with large contents of solids are often homogenized in nonpolar solvents like hexane, while for samples with high water content dissolution in acids, bases, buffers or very polar solvents such as methanol are recommended.
Additionally, SPE allows one to alter the properties of the sample matrix. If, for example, natural products are extracted with methanol or acetone, the polarity of the extracts can be increased by dilution with water, in order to enhance nonpolar solid-phase extraction on the C18 material.
Chromabond® Polypropylene Columns
|
|
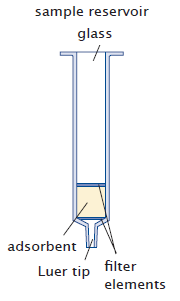 |
Chromabond® Glass Columns
|
Chromafix® Cartridges
|
|
Chromabond® LV Columns
|
|
Chromabond® Multi 96- SPE in 96-Well format
|


