NUCLEOSHELL® – RP 18
Blends Innovative Silica Technology with Excellent Surface Deactivation
Features:
- Based on core-shell particle technology for fast and efficient HPLC
- Suitable for LC/MS and HPLC at pH extremes (pH 1-11)
- Superior base deactivation, ideal for method development
Technical Characteristics:
Octadecyl modification, multiendcapped; pore size 90 Å, particle size 2.7 µm, carbon content 7.5%
Recommended Application:
Overall sophisticated analytical separations, e.g., analgesics, anti -inflammatory drugs, antidepressants; herbicides; phytopharmaceuticals; immunosuppressants
NUCLEOSHELL RP 18 combines innovative silica technology and excellent surface deactivation, that outperforms conventional C18 silicas in terms of efficiency, resolution and speed.
The applied core-shell particle design allows back pressure to provide elevated flow rates that remains at a moderate level and permits the use of existing HPLC equipment in many cases. NUCLEOSHELL RP 18 delivers:
- Extended pH stability
- Low bleed characteristics in LC/MS applications
- Overall robustness, making it an ideal tool for method development and routine analysis in modern HPLC
NUCLEOSHELL RP 18 is based on core-shell particle technology silica. A unique derivatization process generates a homogeneous surface with a high density of bonded silanes (carbon content ~7.5%).
Endcapping suppresses any unwanted polar interactions between the silica surface and sample, which makes NUCLEOSHELL RP 18 particularly suitable for separating basic and other ionizable analytes.
The extremely reduced silanol activity of the phase can be demonstrated by applying basic analytes, such as
tricyclic antidepressants.
Tanaka plot of NUCLEOSHELL RP 18 The diagram below underlines the distinct hydrophobic characteristics and the low silanol activity of the stationary phase.

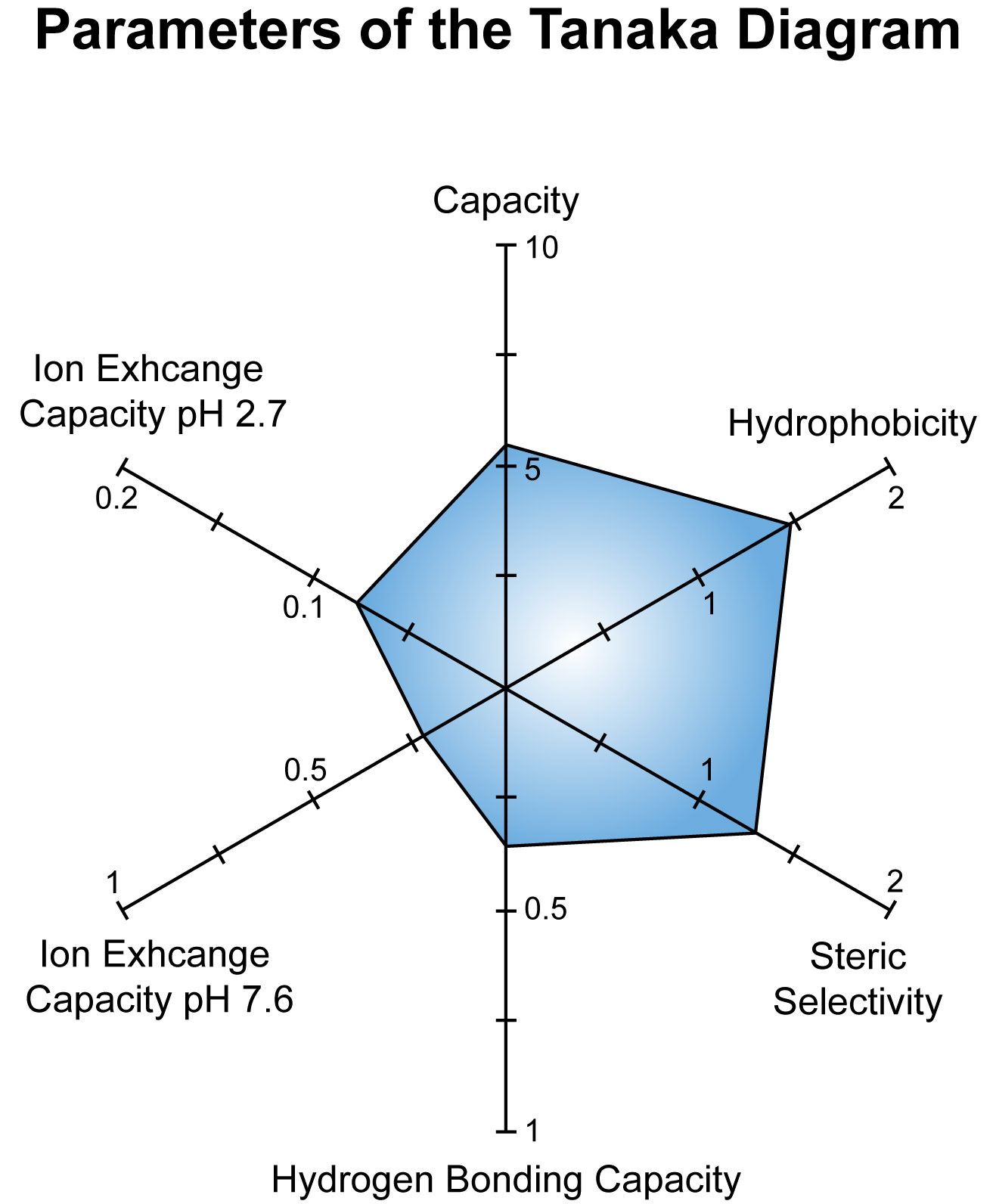
Capacity = k'(pentylbenzene)
Hydrophobicity = α(pentylbenzene, butylbenzene)
Steric selectivity = α(triphenylene, o-terphenyl)
Hydrogen bonding capacity (silanol capacity) = α(caffeine, phenol)
Ion exchange capacity at 2 different pH values (2.7 and 7.6) = α(benzylamine, phenol)
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 763132.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 2x50mm |  Buy now $915.00 Buy now $915.00 |
| 763134.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 2x100mm | |
| 763136.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 2x150mm | |
| 763132.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 3x50mm |  Buy now $915.00 Buy now $915.00 |
| 763134.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 3x100mm | |
| 763136.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 3x150mm | |
| 763132.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 4x50mm |  Buy now $915.00 Buy now $915.00 |
| 763134.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 4x100mm | |
| 763136.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 4x150mm | |
| 763132.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 4.6x50mm |  Buy now $990.00 Buy now $990.00 |
| 763134.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 4.6x100mm | |
| 763136.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 4.6x150mm |
Guard Columns
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 763138.20 | MN HPLC Guard Cartridges, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 2x4mm, 3/pk |  Buy now $201.00 Buy now $201.00 |
| 763138.30 | MN HPLC Guard Cartridges, Nucleoshell RP 18, 90A, 2.7um, 3x4mm, 3/pk |  Buy now $201.00 Buy now $201.00 |


