NUCLEODUR® – HILIC
Features:
- Ideal for reproducible and stable chromatography of highly polar analytes
- Suitable for analytical and preparative applications as well as LC-MS
- Very short column conditioning period
Technical Characteristics:
Ammonium-sulfonic acid modified silica; pore size 110 Å; particle sizes 1, 8, 3, and 5 µm; carbon content 7%; pH stability 2-8.5.
Recommended Application:
Hydrophilic compounds such as organic polar acids and bases, polar natural compounds, nucleosides, oligonucleotides, amino acids, peptides, water-soluble vitamins.
Separation science is always looking for new and effective strategies to accomplish the tasks of modern analytics. Especially for polar compounds reversed-phase HPLC-the most common analytical method-is often limited. Here, hydrophilic stationary phases provide an additional tool for the separation of polar analytes in HPLC.
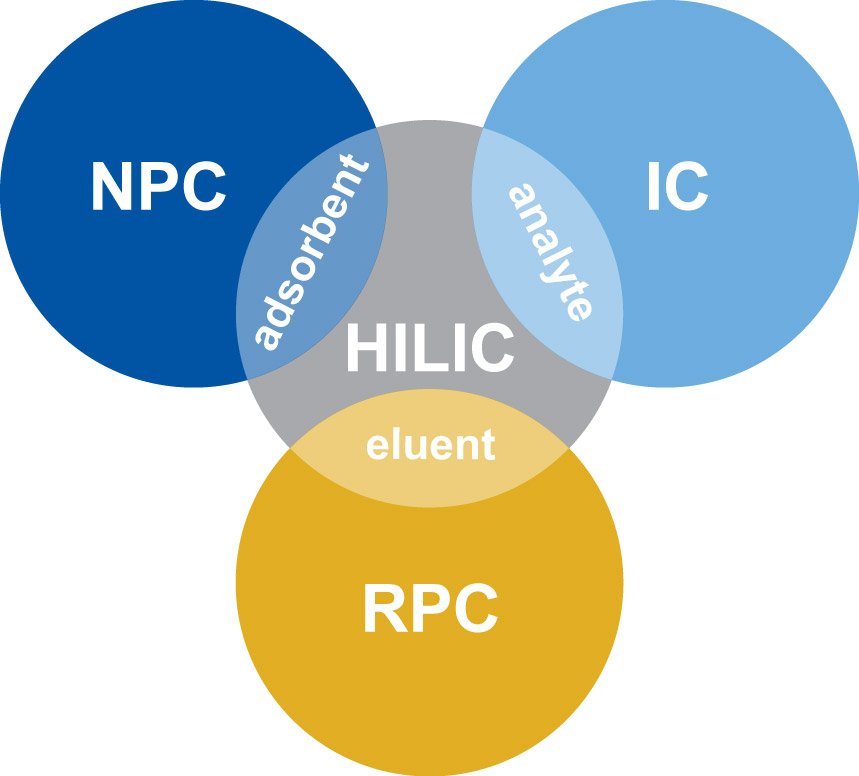
HILIC combines the characteristics of the 3 major methods in liquid chromatography-reversed phase (RPC), normal phase (NPC) and ion chromatography (IC):
- Stationary phases (adsorbents) are mostly polar modifications of silica or polymers (SiOH, NH2, Diol, (zwitter) ions,…)-like in NPC
- Mobile phases (eluents) are mixtures of aqueous buffer systems and organic modifier like acetonitrile or methanol-like in RPC
- Fields of application include quite polar compounds as well as organic and inorganic ions-like in IC
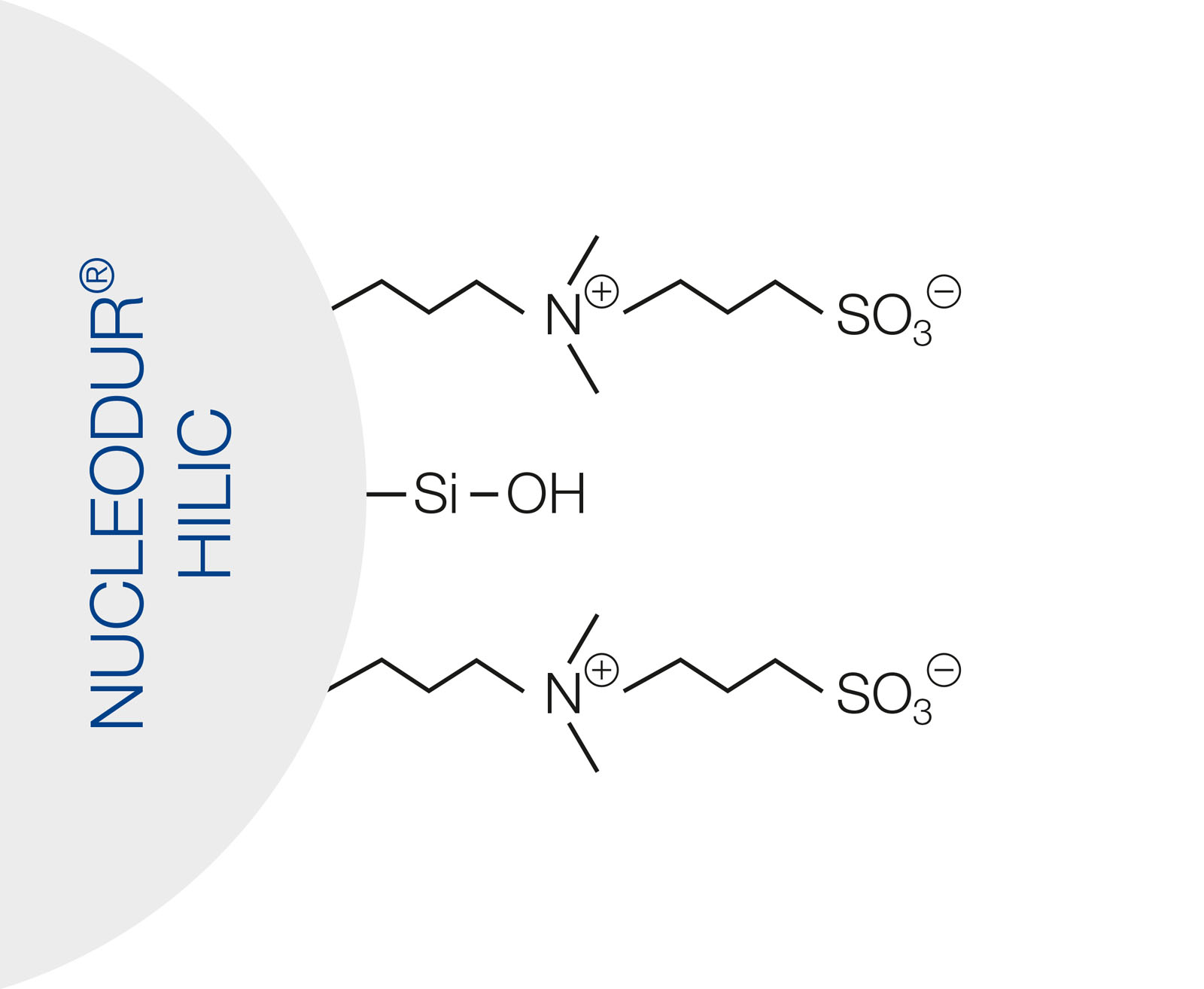
NUCLEODUR HILIC is a special zwitterionic modified stationary phase based on ultra spherical NUCLEODUR particles.
The betaine character of the ammonium-sulfonic acid ligands results in total charge equalization and in neutrally charged but highly polar surface.
Retention Characteristic:
Commonly HILIC is described as partition chromatography or liquid/liquid extraction system between the mobile and stationary phases. Versus a water-poor mobile phase, a water-rich layer on the surface of the polar stationary phase is formed. A distribution of the analytes between these two layers will occur.
HILIC includes weak electrostatic mechanisms as well as hydrogen donor interactions between neutral polar molecules under high organic elution conditions.
This distinguishes HILIC from the ion-exchange chromatography-main principle for HILIC separation is based on compound’s polarity and degree of solvation. More polar compounds will have a stronger interaction with the stationary aqueous layer than less polar compounds-resulting in stronger retention.

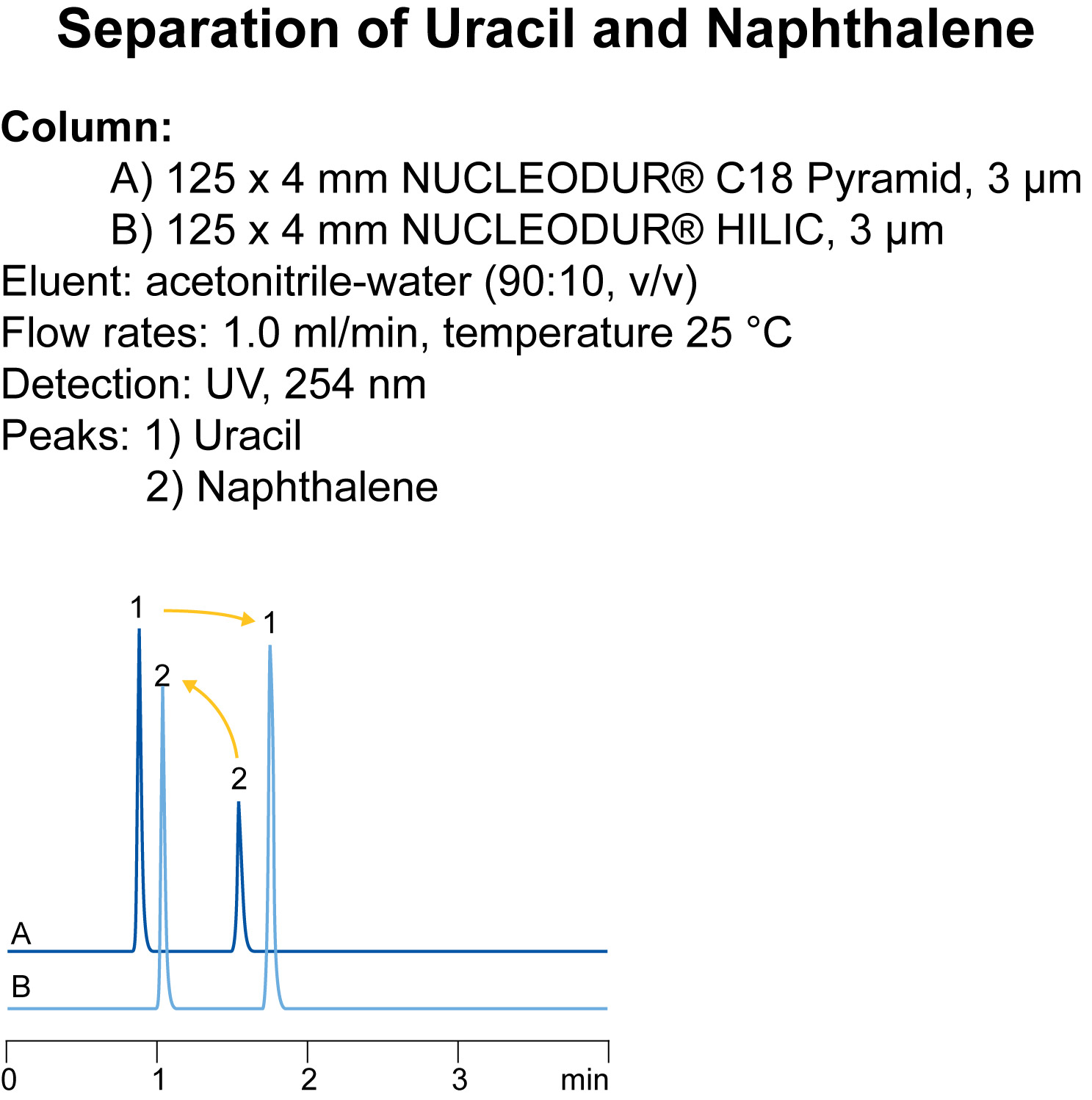
Nonpolar compounds exhibit faster elution profiles due to minor hydrophobic interactions. As shown for the separation of uracil and naphthalene the elution order is quite often inverse on HILIC columns compared to RP columns.
This compares to medium polar aminopropyl phases or modification with less balanced charge equalization. NUCLEODUR® HILIC shows a superb separation and peak shape for critical compounds like adenosine phosphates.
Stability Features:
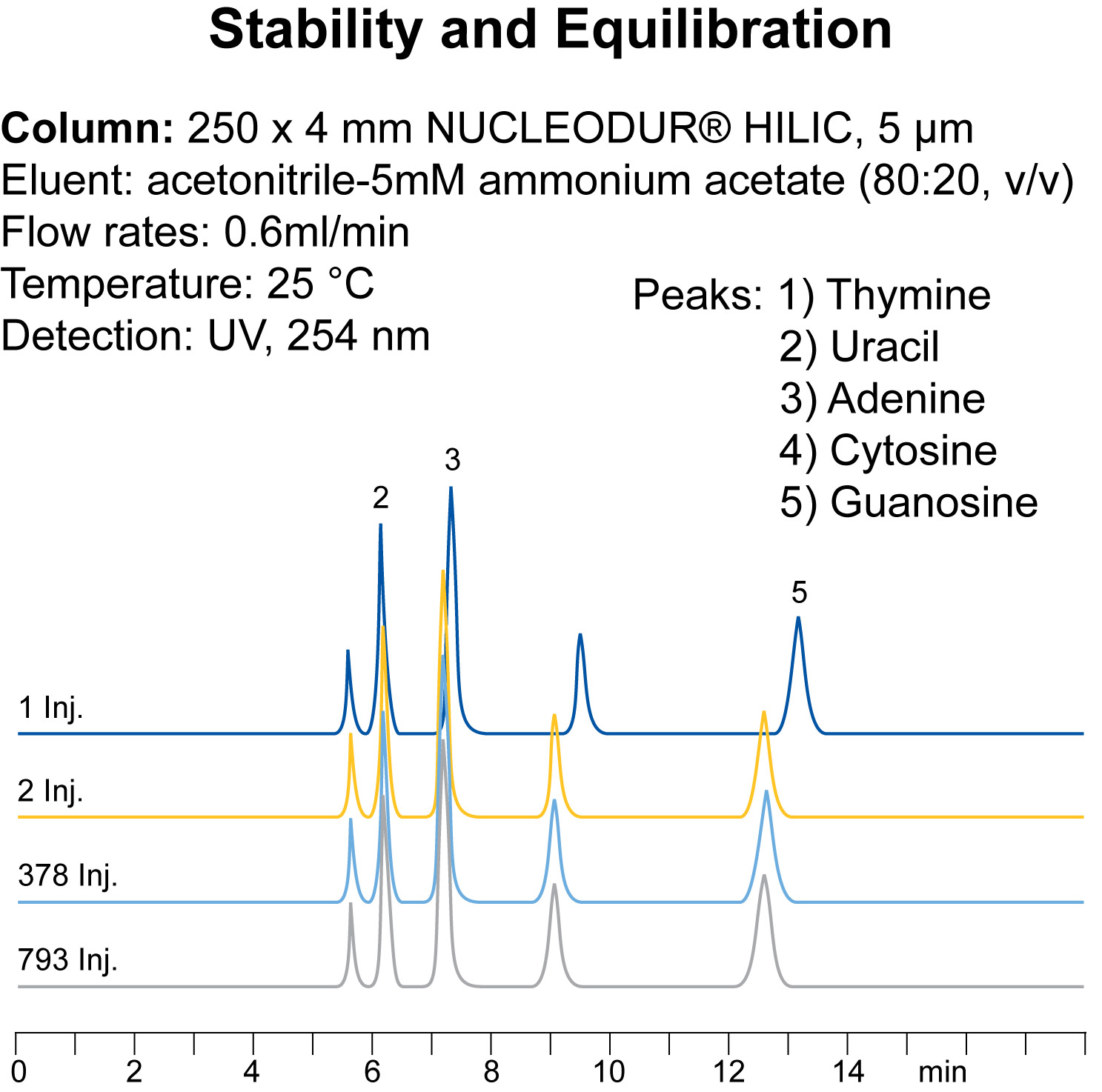
Due to an advanced and unique surface modification procedure (pat. pend.) NUCLEODUR HILIC columns provide short equilibration times-after just 20 min equilibration already the 2nd injection shows stable and reproducible results.
Beyond this, NUCLEODUR HILIC columns are characterized by an outstanding column life time-even after nearly 800 runs the columns show no loss of pristine performance-peak shape and retention are still immaculate.
Due to its high loadability NUCLEODUR HILIC is absolutely suitable for preparative and semi-preparative applications.
1.8um
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 760521.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 2x30mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760523.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 2x50mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760525.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 2x75mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760526.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 2x100mm | |
| 760528.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 2x150mm | |
| 760521.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 3x30mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760523.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 3x50mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760521.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 4x30mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760523.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 4x50mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760521.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 4.6x30mm | |
| 760523.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 1.8um, 4.6x50mm |
3um
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 760531.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 2x125mm | |
| 760533.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 2x150mm | |
| 760532.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 3x50mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760530.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 3x250mm | |
| 760532.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4x50mm |  Buy now $950.00 Buy now $950.00 |
| 760531.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4x125mm | |
| 760533.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4x150mm | |
| 760530.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4x250mm | |
| 760532.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4.6x50mm | |
| 760534.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4.6x100mm | |
| 760531.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4.6x125mm | |
| 760533.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4.6x150mm | |
| 760530.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 3um, 4.6x250mm |
5um
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 760552.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 2x50mm |  Buy now $755.00 Buy now $755.00 |
| 760551.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 2x125mm |  Buy now $860.00 Buy now $860.00 |
| 760553.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 2x150mm |  Buy now $860.00 Buy now $860.00 |
| 760550.20 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 2x250mm |  Buy now $990.00 Buy now $990.00 |
| 760552.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 3x50mm |  Buy now $760.00 Buy now $760.00 |
| 760551.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 3x125mm |  Buy now $870.00 Buy now $870.00 |
| 760553.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 3x150mm |  Buy now $870.00 Buy now $870.00 |
| 760550.30 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 3x250mm |  Buy now $985.00 Buy now $985.00 |
| 760552.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4x50mm |  Buy now $760.00 Buy now $760.00 |
| 760551.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4x125mm |  Buy now $870.00 Buy now $870.00 |
| 760553.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4x150mm |  Buy now $870.00 Buy now $870.00 |
| 760550.40 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4x250mm |  Buy now $985.00 Buy now $985.00 |
| 760552.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4.6x50mm |  Buy now $825.00 Buy now $825.00 |
| 760554.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4.6x100mm |  Buy now $955.00 Buy now $955.00 |
| 760551.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4.6x125mm |  Buy now $955.00 Buy now $955.00 |
| 760553.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4.6x150mm |  Buy now $955.00 Buy now $955.00 |
| 760550.46 | MN HPLC Column, Nucleodur HILIC, 110A, 5um, 4.6x250mm |
Guard Cartridges
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 761960.20 | MN HPLC Guard Cartridges, Nucleodur HILIC, 1.8um, 2x4mm, 3/pk |  Buy now $206.00 Buy now $206.00 |
| 761960.30 | MN HPLC Guard Cartridges, Nucleodur HILIC, 1.8um, 3x4mm, 3/pk |  Buy now $206.00 Buy now $206.00 |
| 761961.20 | MN HPLC Guard Cartridges, Nucleodur HILIC, 3um, 2x4mm, 3/pk |  Buy now $206.00 Buy now $206.00 |
| 761961.30 | MN HPLC Guard Cartridges, Nucleodur HILIC, 3um, 3x4mm, 3/pk |  Buy now $206.00 Buy now $206.00 |
| 761962.20 | MN HPLC Guard Cartridges, Nucleodur HILIC, 5um, 2x4mm, 3/pk |  Buy now $206.00 Buy now $206.00 |
| 761962.30 | MN HPLC Guard Cartridges, Nucleodur HILIC, 5um, 3x4mm, 3/pk |  Buy now $206.00 Buy now $206.00 |


