C18 HPLC Analytical
C18 silica gel is the most popular and versatile Reversed Phase, capable of hydrophobic interactions with a wide variety of organic compounds.
C18 silica gel is used for Reversed Phase chromatography for the separation of nonpolar to moderately polar compounds such as: Fatty acids, glycerides, Polycyclic aromatics, Esters (Phthalates), Fat-soluble vitamins, Steroids, Prostaglandins, and PTH amino acids.
Other recommended applications: Catecholamines, drugs, drug metabolites, dyes, pesticides, PCBs, antiarrhythmics.
For HPLC, UHPLC, SFC, or Capillary LC
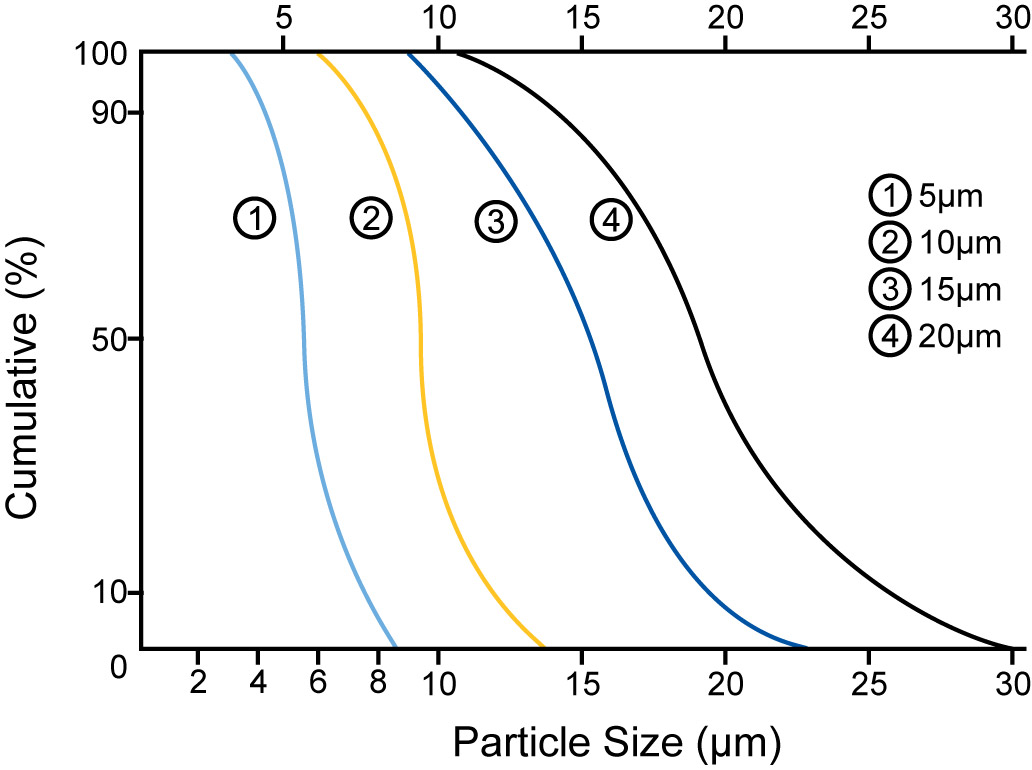
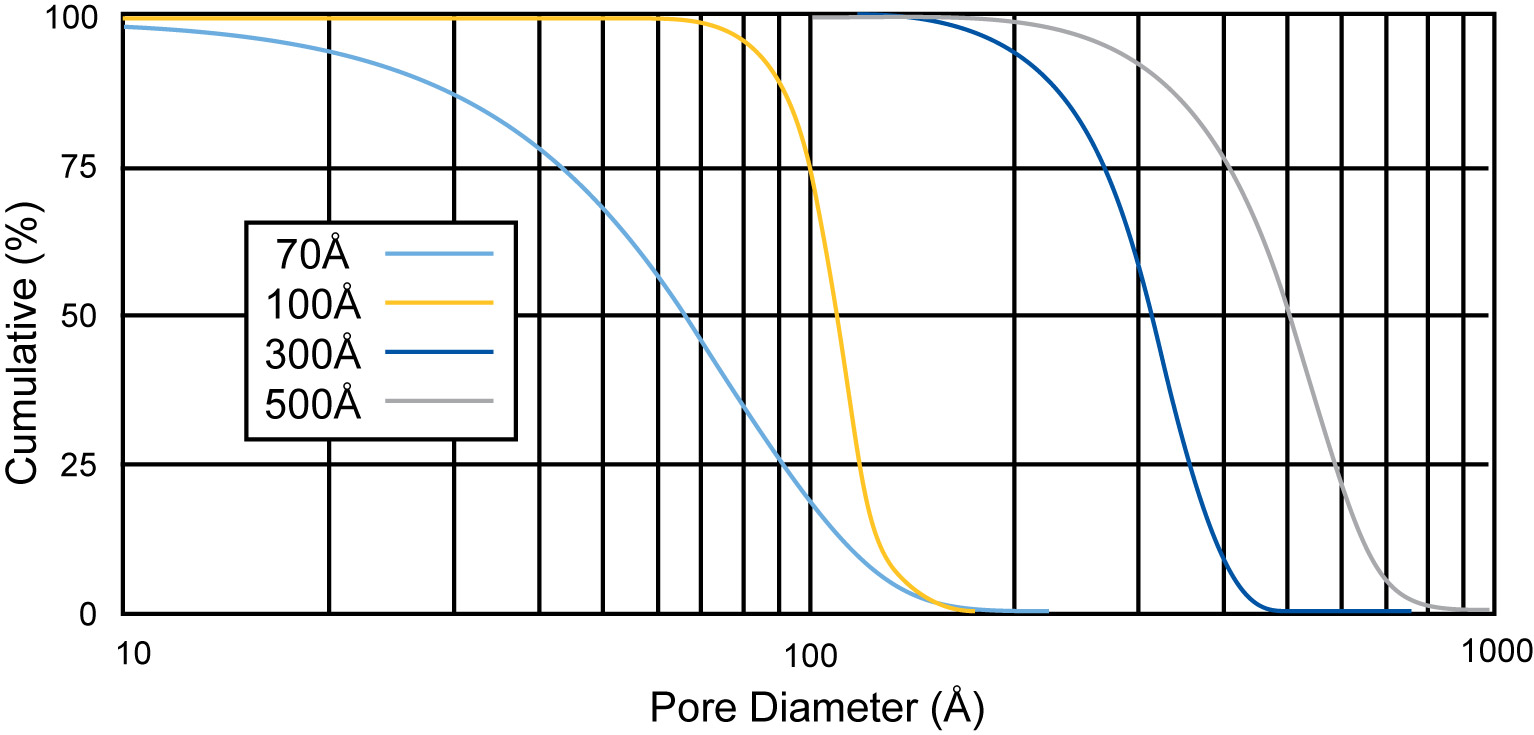
C18 HPLC Analytical is available in porosities of 100Å, 150Å, 200Å, and 300Å and particle sizes of 2µm, 3µm, 5µm, and 10µm.
Quality and Diversity
C18 HPLC Analytical is manufactured on Sorbtech’s Premium Pure™ Spherical Silica Gel which boasts very narrow pore and particle distributions, ensuring optimal selectivity, capacity, efficiency, low operating pressure, shorter processing time; and are therefore, the best balance between high performance and value.
Purity
Premium Pure Spherical Silica Gel is manufactured to a very high chemical purity standard (>99.99% SiO2). Organics and trace metals content are controlled within stringent limits. Each production batch has undergone extensive quality control testing to ensure reliable lot-to-lot performance. This rigid control of chemical purity, surface area and pore size, ensure our silica will yield reproducible separation results and allow for direct scale-up without requiring time-consuming method redevelopment.
Robust
Our spherical silicas are mechanically robust and can, therefore, be repacked multiple times in either analytical or preparative scale columns.
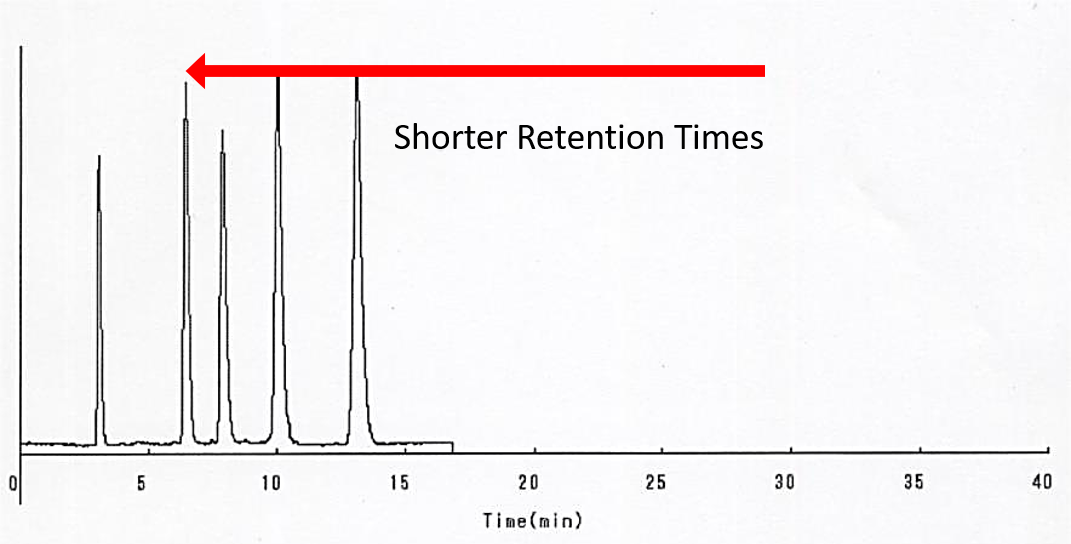
Example 1 – Shorten Retention Times with C18AQ – C18 MNE vs. C18AQ
The example below compares a C18 Silica Gel to a C18 Aqueous Silica Gel. Both phases were applied to the same base silica gel. All conditions are the same. The retention times of the C18 Aqueous are reduced due to the shielding of silanol groups on the silica surface by the endcapping reagent that introduces highly polar terminal groups. The result is shorter retention times.
C18 MNE, 100A, 5um – Carbon Content: 15.2%
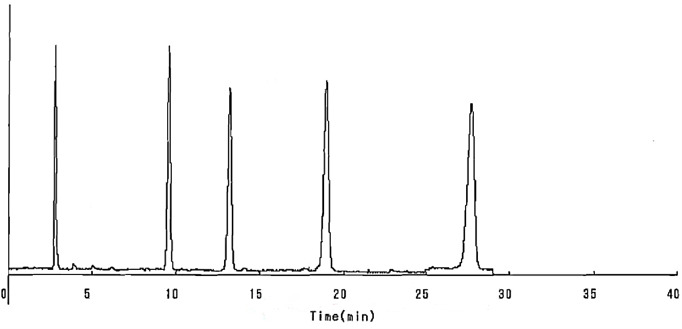
C18 Aqueous, 100A, 5um – Carbon Content: 11.1%
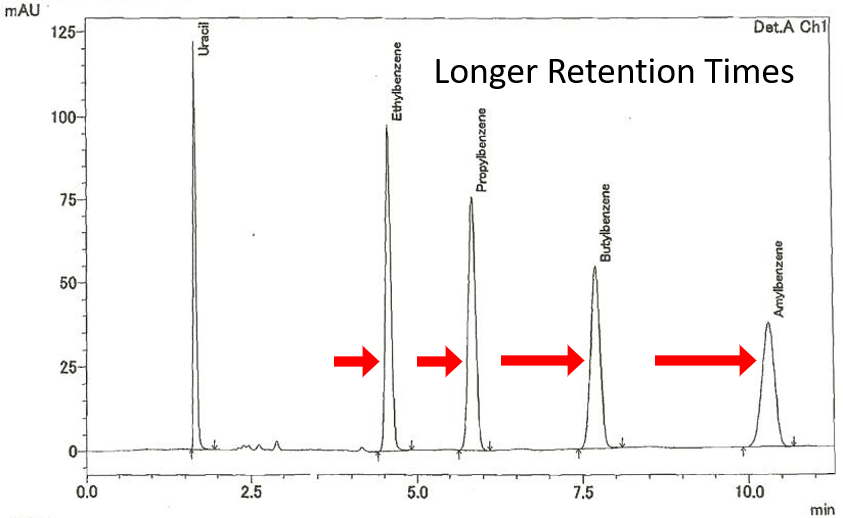
Example 2 – Higher Retention Times with Better Endcapping – C18 MNE vs. C18MHE
The example below compares a C18 Silica Gel to a C18 Silica Gel with high endcapping. Both phases were applied to the same base silica gel. With all conditions equal, the increase of shielded silanol groups with highly non-polar terminal groups on the silica surface resulted in higher retention times.
C18 MNE, 100A, 5um – Carbon Content: 16%
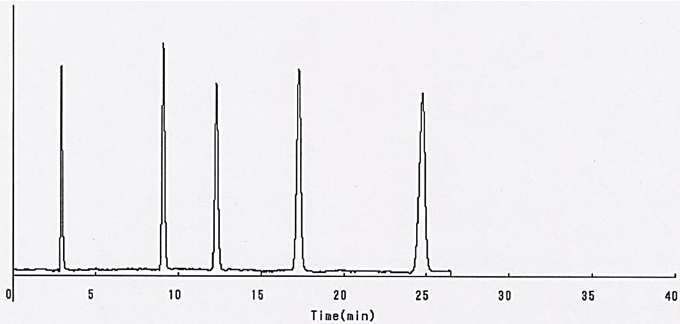
C18 MHE, 100A, 5um – Carbon Content: 16.1%
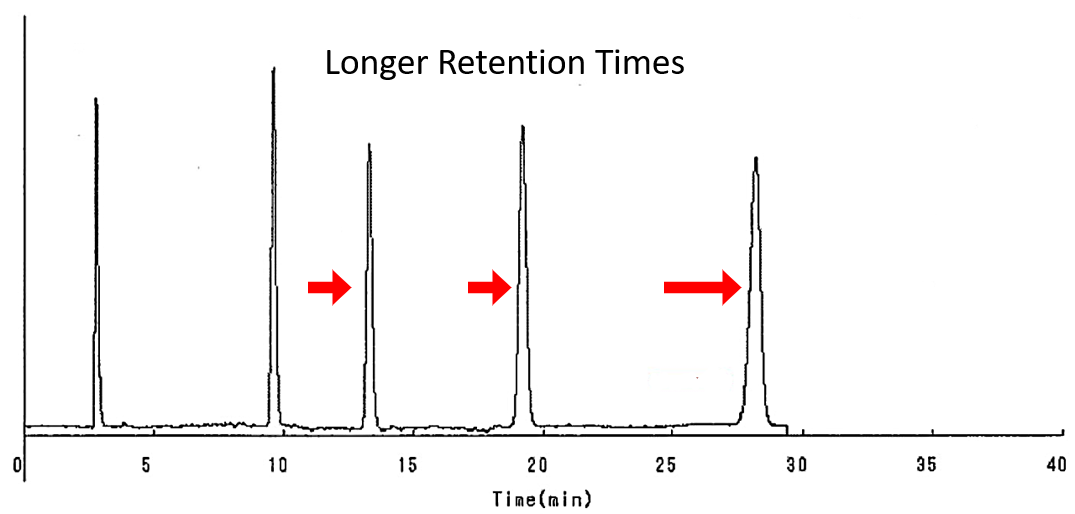
Example 3 – Higher Retention Times with Higher Carbon Load – C18AQ vs. C18AQ II
The example below compares a C18 Aqueous Silica Gel to a C18 Aqueous II Silica Gel. Both phases were applied to the same base silica gel. With all conditions equal, the higher carbon loading resulted in higher retention times.
C18 Aqueous, 100A, 5um – Carbon Content: 11.0%
C18 Aqueous II, 100A, 5um – Carbon Content: 13.4%
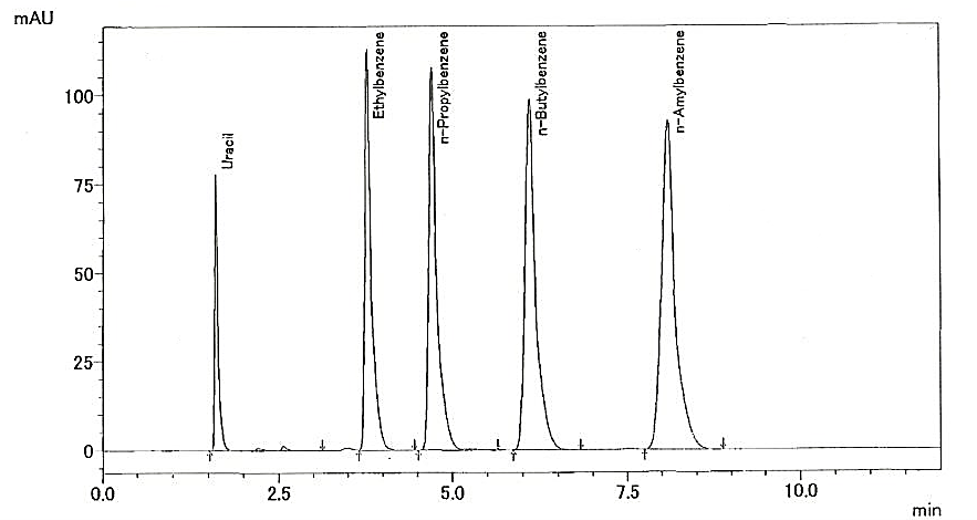
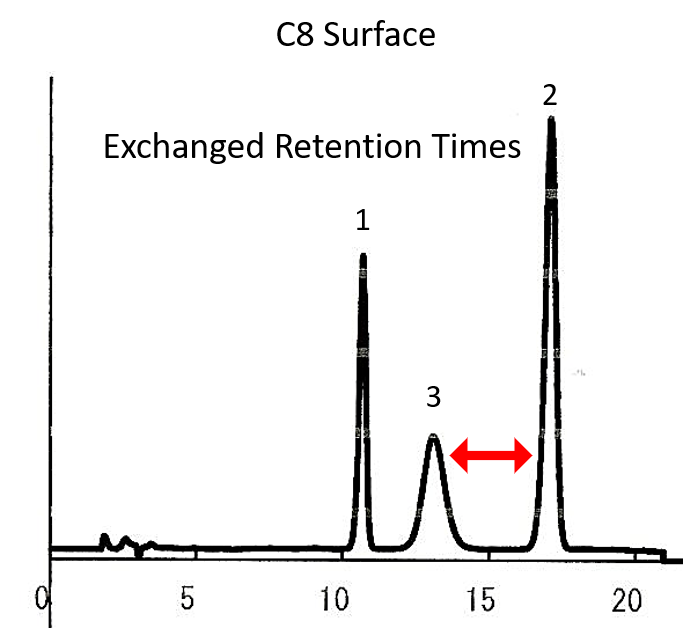
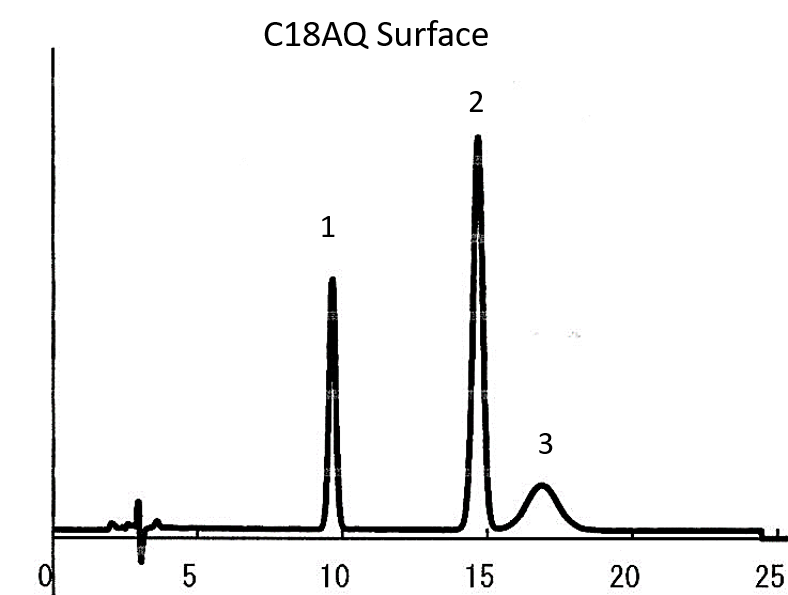
Example 4 – Better Selectivity with Similar Carbon Loading – C8 vs. C18AQ
The example below compares a C8 Silica Gel to a C18 Aqueous Silica Gel. Both phases were applied to the same base silica gel. Even though the two adsorbents have comparable carbon loading percentages, the result was a difference in selectivity. By something as simple as changing the stationary phase while keeping all conditions the same, the end user can solve or improve chromatographic results.
100Å
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 10302050-001 | C18 TNE (Trifunctional Non-Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 3um, 10g | |
| 10301546-001 | C18 MLE (Monofunctional Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 2um, 10g |  Buy now $482.10 Buy now $482.10 |
| 10302046-001 | C18 MLE (Monofunctional Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 3um, 10g |  Buy now $455.05 Buy now $455.05 |
| 10304046-001 | C18 MLE (Monofunctional Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 10um, 10g |  Buy now $289.50 Buy now $289.50 |
| 10302049-001 | C18 Aqueous II Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 3um, 10g | |
| 10304052-001 | C18 THE (Trifunctional Hi Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 10um, 10g |  Buy now $359.63 Buy now $359.63 |
| 10303046-001 | C18 MLE (Monofunctional Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 5um, 10g |  Buy now $392.89 Buy now $392.89 |
| 10304047-001 | C18 MHE (Monofunctional Hi Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 10um, 10g |  Buy now $342.00 Buy now $342.00 |
| 10304049-001 | C18 Aqueous II Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 100A, 10um, 10g |  Buy now $315.75 Buy now $315.75 |
150Å
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 10352049-001 | C18 Aqueous II Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 150A, 3um, 10g | |
| 10353049-001 | C18 Aqueous II Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 150A, 5um, 10g |
300Å
| Catalog No. | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 10502046-001 | C18 MLE (Monofunctional Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 300A, 3um, 10g | |
| 10503046-001 | C18 MLE (Monofunctional Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 300A, 5um, 10g | |
| 10504046-001 | C18 MLE (Monofunctional Endcapped) Spherical Silica Gel, Premium Pure, 300A, 10um, 10g |


